Shared Earth

Amur Leopard
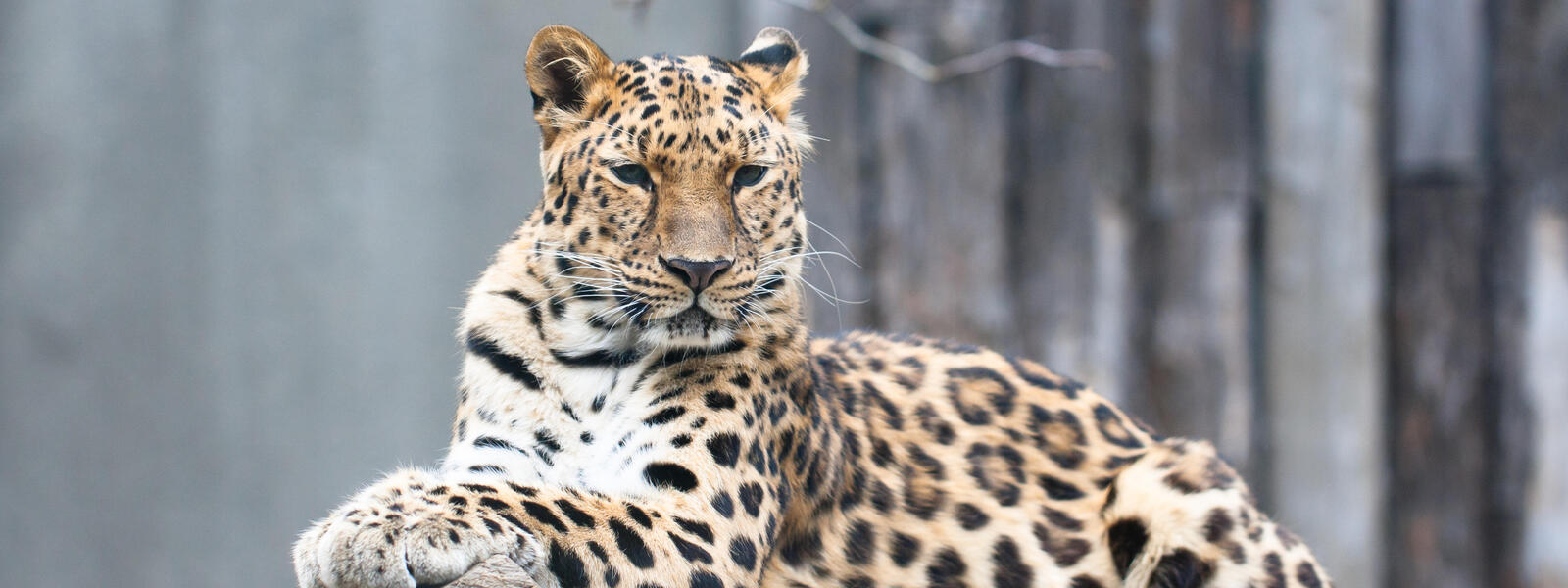

People usually think of leopards in the savannas of Africa but in the Russian Far East, a rare subspecies has adapted to life in the temperate forests that make up the northern-most part of the species’ range. Similar to other leopards, the Amur leopard can run at speeds of up to 37 miles per hour. This incredible animal has been reported to leap more than 19 feet horizontally and up to 10 feet vertically. The Amur leopard is solitary. Nimble-footed and strong, it carries and hides unfinished kills so that they are not taken by other predators. It has been reported that some males stay with females after mating, and may even help with rearing the young. Several males sometimes follow and fight over a female. They live for 10-15 years, and in captivity up to 20 years. The Amur leopard is also known as the Far East leopard, the Manchurian leopard or the Korean leopard.
Why they are endangered
Lack of prey to sustain the large populations of leopards and tigers along with illegal poaching for the Amur leopard’s skin.
Unlike other leopards living in the savanna, the Amur leopard has well adapted itself into the temperate forests and cold climates of its region. Therefore they have thick fur which grows up to 7.5 cm long in winter, providing them with warmth and camouflage. The Amur leopard also chooses to carry out unfinished kills so that they aren’t taken by other predators. However, just like other leopards, the Amur leopard is capable of running at speeds of 37 miles per hour along with the ability of being able to leap more than 19 feet horizontally and up to 10 feet vertically. The Amur leopard lives up to 10-15 years and tends to weigh 23-48 kg.
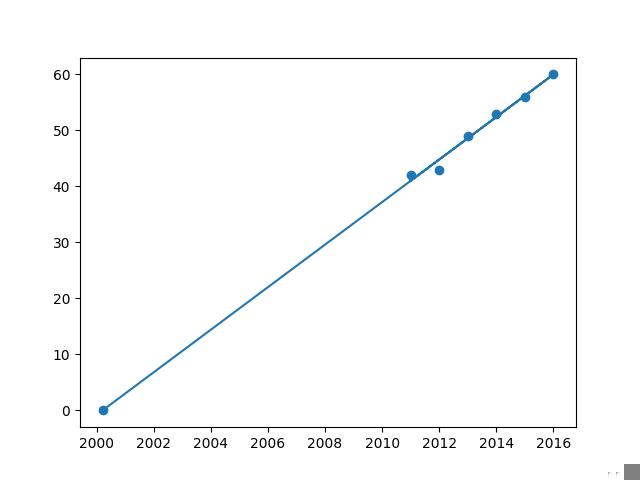
Linear-regression predicting model--number of Amur Leopard vs relative years